The Unsung Hero of the Hand: Unlocking the Power of the Palmaris Longus Muscle
The human body is a complex machine, with over 600 muscles that work together to enable movement, maintain posture, and facilitate daily activities. While some muscles are well-known for their prominent roles, others remain in the shadows, waiting to be discovered. One such muscle is the palmaris longus, a small but mighty flexor that plays a crucial role in the hand's anatomy. In this article, we'll delve into the world of the palmaris longus muscle, exploring its functions, location, and significance in maintaining hand health.
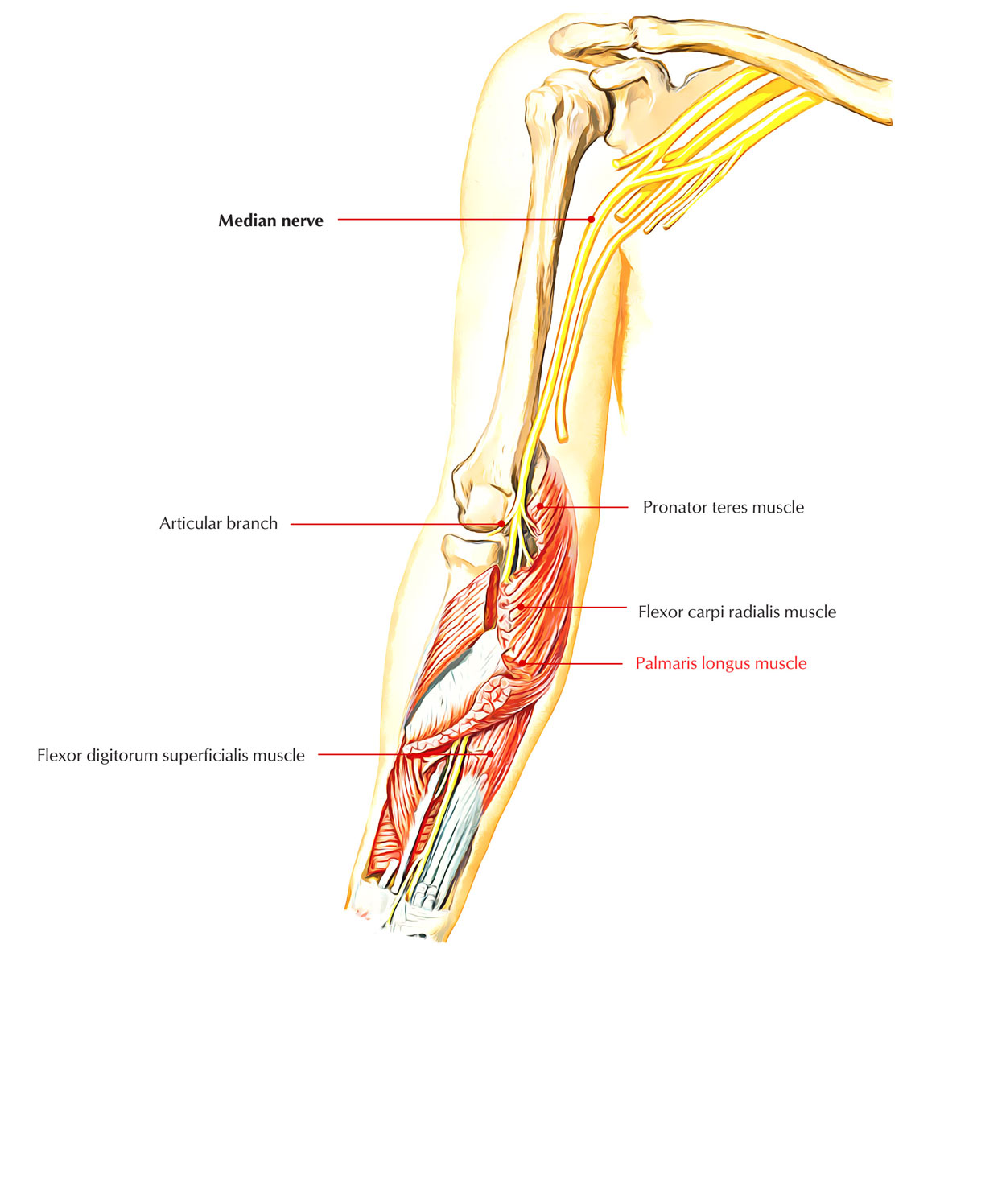
The palmaris longus muscle is a relatively small muscle located in the forearm, extending from the middle third of the ulna bone to the wrist. Despite its compact size, it plays a vital role in flexing the wrist and fingers, enabling us to grasp and manipulate objects. This muscle is part of the anterior forearm muscles, which work together to facilitate movements such as flexion, extension, and rotation.
The palmaris longus muscle is often considered an accessory muscle of the flexor carpi radialis, a more prominent flexor muscle in the forearm. However, this doesn't diminish its importance, as the palmaris longus contributes significantly to the hand's overall flexibility and dexterity. In fact, research suggests that the palmaris longus muscle is more sensitive to fatigue than the flexor carpi radialis, making it a key player in maintaining hand function over time.
Location of the Palmaris Longus Muscle
The palmaris longus muscle is located in the forearm, running from the middle third of the ulna bone to the wrist. It originates from the middle third of the ulna and inserts into the palmar aponeurosis, a fibrous tissue that forms the palmar surface of the hand. This unique location allows the palmaris longus muscle to work in conjunction with other muscles to facilitate wrist and finger movement.
The palmaris longus muscle is surrounded by other important structures in the forearm, including the brachial artery, median nerve, and flexor tendons. Understanding the relationships between these structures is essential for grasping the functions of the palmaris longus muscle.
Functions of the Palmaris Longus Muscle
The palmaris longus muscle plays a crucial role in flexing the wrist and fingers, enabling us to perform various daily activities such as grasping, gripping, and manipulating objects. Its primary functions include:
• Wrist flexion: The palmaris longus muscle helps to flex the wrist, allowing us to bend our wrist towards the palm of the hand.
• Finger flexion: This muscle also assists in flexing the fingers, enabling us to curl our fingers into a fist or grasp small objects.
• Elbow flexion: Although not its primary function, the palmaris longus muscle also contributes to elbow flexion, helping to bend the elbow joint.
Damage to the Palmaris Longus Muscle
While the palmaris longus muscle is relatively small, damage to this muscle can have significant consequences for hand function. One common cause of palmaris longus injury is tennis elbow, a condition characterized by inflammation and irritation of the tendons in the forearm. This condition can be caused by repetitive strain, overuse, or poor technique.
Other injuries to the palmaris longus muscle include strains, sprains, and tears. These injuries can be caused by various factors, including trauma, overuse, or poor posture. If left untreated, these injuries can lead to chronic pain, limited mobility, and reduced grip strength.
Prevention and Treatment of Palmaris Longus Muscle Injuries
Preventing injuries to the palmaris longus muscle is essential for maintaining hand health. Here are some ways to prevent and treat palmaris longus muscle injuries:
• Warm-up and stretching: Engage in regular warm-up and stretching exercises to improve flexibility and reduce the risk of injury.
• Proper technique: Use proper technique when performing activities that involve wrist and finger movement, such as playing sports or using heavy tools.
• Strengthening exercises: Engage in strengthening exercises to improve hand strength and flexibility.
• Rest and recovery: Allow adequate rest and recovery time to prevent overuse and fatigue.
Treatment options for palmaris longus muscle injuries include:
• Physical therapy: A physical therapist can help develop a customized exercise program to improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
• Rest and ice: Apply ice to the affected area to reduce pain and inflammation.
• Pain management: Over-the-counter pain medications can help manage pain and discomfort.
• Bracing and supports: Wear a wrist splint or use a supportive brace to provide stability and support.
Conclusion
The palmaris longus muscle is a vital component of the hand's anatomy, playing a crucial role in wrist and finger movement. While it may be a small muscle, its importance cannot be overstated. By understanding the functions, location, and significance of the palmaris longus muscle, we can appreciate the complexity of the human body and take steps to maintain hand health. Whether you're an athlete, a musician, or simply someone who enjoys a good meal, maintaining hand health is essential for optimal function and quality of life.
Anatomy of the Palmaris Longus Muscle
The palmaris longus muscle is a long, thin muscle that runs from the middle third of the ulna bone to the wrist. Its unique location allows it to work in conjunction with other muscles to facilitate wrist and finger movement.
Attachment Points
The palmaris longus muscle attaches to the palmar aponeurosis, a fibrous tissue that forms the palmar surface of the hand. It also attaches to the tendon of the flexor carpi radialis, a more prominent flexor muscle
Kimol Song
Tim Miller Tyler Jameson Wedding
Aaron Judge Brother
Article Recommendations
- Localeo Rank Checker
- Who Is Brian Adams Partner
- Talia Ryder
- Naomi Wattsx Husband
- Markavis Girlfriend
- Camila Araujo Fans
- Beatrice Minns
- Jackoherty Girlfriend
- Maryarps Partner
- Danielaenby Ashe