California Earthquake: A Powerful Quake Rocks the State
California has long been known for its volatile tectonic plate system, making it one of the most seismically active regions in the world. The state's unique geography, with its intersection of several major fault lines, creates a high-risk environment for earthquakes. On [Date], a powerful earthquake struck California, leaving a trail of destruction and chaos in its wake. The quake, which had a magnitude of [Magnitude], was felt throughout the state, causing widespread panic and disruption to daily life.
The California earthquake was a major event that served as a stark reminder of the state's seismic risks. With its diverse geography, which includes mountains, valleys, and coastlines, California is prone to a wide range of earthquakes, from small tremors to devastating quakes. The state's earthquake risk is further exacerbated by its dense population, with millions of people living in areas prone to seismic activity.
Geology of California Earthquakes
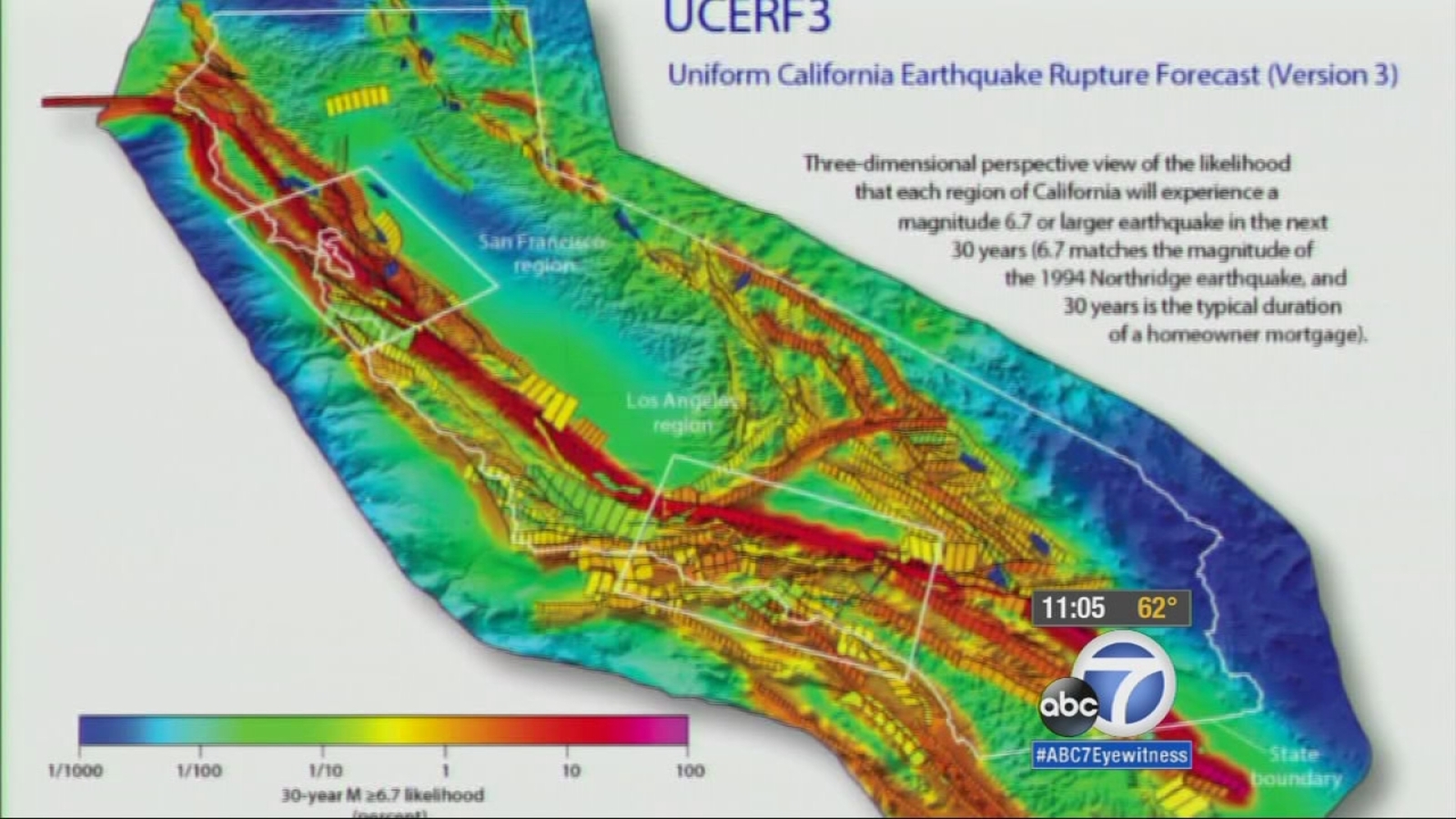
California's earthquake-prone history is rooted in its geology. The state is situated on the boundary between the Pacific and North American tectonic plates, which meet at the San Andreas Fault. This fault line stretches over 800 miles (1,300 km) through California, providing a conduit for the movement of tectonic plates. As the Pacific plate moves northwest relative to the North American plate, it pulls on the Earth's crust, creating stress that is released as earthquakes.
Major Fault Lines
California is home to several major fault lines, including the San Andreas Fault, the Hayward Fault, and the Calaveras Fault. These fault lines are capable of producing large, destructive earthquakes. The San Andreas Fault, for example, is one of the most famous fault lines in the world and is responsible for many of the state's most significant earthquakes, including the 1906 San Francisco earthquake and the 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake.
Lesser-Known Fault Lines
While the San Andreas Fault is the most well-known, there are several lesser-known fault lines in California that are equally capable of producing significant earthquakes. The Hayward Fault, for example, runs through the San Francisco Bay Area and has a history of producing strong earthquakes. The Calaveras Fault, which runs through the Sierra Nevada mountains, is also capable of producing significant earthquakes.
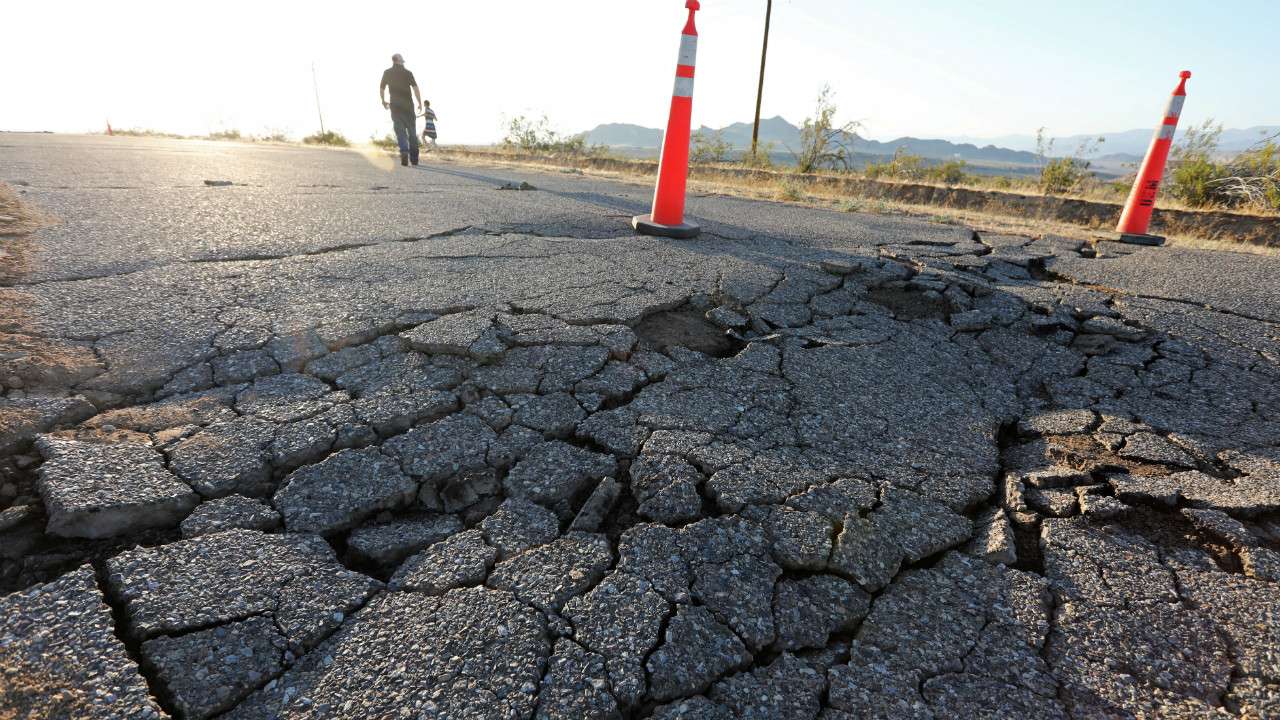
Impact of the Earthquake
The California earthquake had a significant impact on the state's residents, businesses, and infrastructure. The quake caused widespread damage to buildings, roads, and other infrastructure, with some areas reporting significant destruction. Emergency services were quickly overwhelmed, with firefighters, paramedics, and police officers working to rescue those trapped in debris.
Economic Impact
The economic impact of the earthquake was significant, with estimates suggesting that the damage could exceed $100 billion. The quake disrupted business operations, with many companies forced to close temporarily due to the damage. The state's tourism industry was also impacted, with many visitors forced to cancel their trips due to the quake.
Infrastructure Damage
The earthquake caused significant damage to California's infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and buildings. Many of the state's major highways were closed due to the damage, causing traffic congestion and disrupting supply chains. The quake also caused significant damage to the state's electrical grid, with many power outages reported.
Response and Recovery Efforts
In the aftermath of the earthquake, the state's emergency services sprang into action, with teams of responders working to rescue those trapped in debris and provide aid to those in need. The state's governor, [Governor's Name], declared a state of emergency, mobilizing resources and personnel to support the response and recovery efforts.
Evacuation and Shelter
Many residents were forced to evacuate their homes, with some areas under mandatory evacuation orders. The state's emergency services set up shelters for those displaced by the quake, with many residents forced to stay in temporary accommodations for several days.
Aid and Assistance
The state's residents and organizations came together to provide aid and assistance to those affected by the earthquake. Many residents donated food, water, and clothing to those in need, while organizations such as the American Red Cross and the Salvation Army provided critical support services.
Conclusion
The California earthquake was a powerful and destructive event that served as a stark reminder of the state's seismic risks. The quake caused significant damage and disruption to daily life, with many residents forced to evacuate their homes and businesses. However, the state's emergency services and residents responded quickly and effectively, with many residents and organizations coming together to provide aid and assistance to those in need.
Next Steps
As the state begins the process of recovery and rebuilding, there are several steps that can be taken to mitigate the risk of future earthquakes. These include:
- Strengthening building codes to ensure that new construction is earthquake-resistant
- Implementing early warning systems to provide residents with critical seconds to seek safety
- Enhancing emergency preparedness and response plans to ensure that residents are prepared for future earthquakes
By taking these steps, California can reduce its risk of earthquake damage and minimize the impact of future quakes.
How Tall Isabrina Carpenter
Rick Harrison Net Worth
Chaun Woo Parents
Article Recommendations
- How Old Iarleyhimkus
- Raiders Owner
- Dididdy Pass Away
- Hisashi Ouchi Real Po
- Rami Malek Portiaoubleday
- Skyes In 2024
- Rebecca Pritchard Illness
- Lane Garrison
- Gaz Coombes Wife
- Google Places Rank Tracking